Bioenergetics is the study of all energy made or lost through chemical bonds in living organisms. This guide will introduce bioenergetics, key terms, and definitions you should remember as you prepare for the MCAT.
Let’s get started!
Bioenergetics on the MCAT: What Do You Need to Know?
Bioenergetics is covered in the Biochemistry section of the MCAT.
Introductory biochemistry accounts for 25% of the Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems section (Bio/Biochem) and 25% of the Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems section (Chem/Phys).
It’s hard to predict the exact number of questions about bioenergetics that will appear on the MCAT. However, you can expect it to appear in both the Bio/Biochem and Chem/Phys sections.
Important Sub-Topics – Bioenergetics
We cannot stress enough the importance of bioenergetics during MCAT prep since it is relevant to general chemistry, another important MCAT topic!
Bioenergetics can be complicated, so let’s break them down into important sub-topics you can concentrate on.
1. Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics of Biological Systems
The study of thermodynamics describes how energy within a system can change. Thermodynamics can be measured, and one example is through Gibbs free energy. Gibbs free energy is used to measure the maximum amount of work done in a thermodynamic system when the temperature and pressure are kept constant.
The change in Gibbs free energy (𝜟G) determines the spontaneity of a biochemical reaction and whether energy has been released or put into the system.
The Change In Gibbs Free Energy (𝜟G) | Spontaneity | Free Energy |
|---|---|---|
Negative 𝜟G | Spontaneous | Exergonic |
Positive 𝜟G | Nonspontaneous | Endergonic |
Full Study Notes : Bioenergetics: Thermodynamics of Biological Systems on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on thermodynamics of Biological systems, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
2. Bioenergetics: Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is the cell’s main energy source. ATP is composed of a ribose sugar with an adenine base attached at the C1 carbon and 3 phosphate groups.
The release of one of these phosphate groups from the ATP molecule results in a considerable energy release. This is seen in both ATP hydrolysis and phosphoryl group transfers.
Full Study Notes : Bioenergetics: Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on adenosine triphosphate (ATP), check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
3. Bioenergetics: Biological Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
A lot of biochemical processes involve the transfer of electrons! This transfer occurs through oxidation-reduction reactions.
Two half reactions exist: oxidation and reduction. In many biochemical reactions, the reduction half-reaction results in the production of high-energy electron carriers.
These are used in many reactions but are most significant in the electron transport chain. Examples include molecules such as Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide.
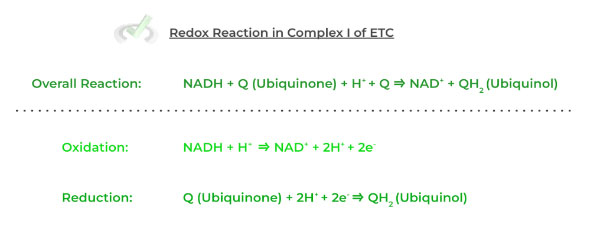
Full Study Notes : Bioenergetics: Biological Oxidation-Reduction Reactions on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review on biological oxidation-reduction reactions, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
Key Terms and Definitions – Bioenergetics
Here are some of the more important key terms and definitions to remember for this general guide to bioenergetics!
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Gibbs free energy | Measures the maximum amount of work done in a thermodynamic system when the temperature and pressure are kept constant. |
Exergonic | Energy is released during the reaction |
Endergonic | Energy is absorbed during the reaction |
Oxidation | Results in the loss of electrons |
Reduction | Results in the gain of electrons |
Additional FAQs – Bioenergetics on the MCAT
What is the difference between bioenergetics and thermodynamics?
What is an example of bioenergetics in biochemistry?
What are the 3 bioenergetic systems?
Is thermodynamics a topic on the MCAT?
Additional Reading Links – Study Notes for Bioenergetics on the MCAT
For more in-depth content review about bioenergetics on the MCAT, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers!
Additional Reading: Biochemistry Subjects on the MCAT:
- Biological Membranes on the MCAT
- Carbohydrate Metabolism on the MCAT
- Carbohydrate Structure on the MCAT
- DNA and RNA on the MCAT
- Enzymes on the MCAT
- Lipids and Lipid Metabolism on the MCAT
- Non-Enzymatic Proteins on the MCAT
- Regulation of Metabolism on the MCAT
- Biotechnology on the MCAT
- Amino Acids Peptides Proteins on the MCAT


 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these