Close your eyes. Give a moment for yourself. Take a deep breath. As important as this technique is, it’s equally as important to know the function of your respiratory system to how it’s able to aid us in calm breathing that will eventually help us on test day!
The respiratory system of course is responsible for our breathing, with our pair of lungs coming to mind as the main organ. However, there are also other functions and nuances in the respiratory system and other bodily structures that play a pivotal role in our breathing physiology!
This guide will introduce you to the basics of the respiratory system, some key ideas and concepts, and how other MCAT subject topics might overlap and play a role in breathing. Let’s get started!
Respiratory System on the MCAT: What You Need To Know
Topics on the respiratory system will be tested on the biology section of the MCAT can appear both as passage based and fundamental discrete questions, but will probably appear more as fundamental discrete questions.
While it’s difficult to say with certainty how many respiratory system questions will appear, we can say the probability of having more than 3 respiratory system questions is very low on average as this is a more low yield MCAT chapter.
Introductory biology account for 65% of the content covered in the Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems section (Bio/Biochem) and 5% of content tested in the Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems (Chem/Phys), and 5% of material on the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior (Psych/Soc).
Important Sub-Topics: Respiratory System
While maybe not as rigorously tested as other biological topics such as the endocrine or nervous system, pay close attention to the amount of overlap with different MCAT subject topics such as nervous system control and gas laws!
As such, only an understanding of the main concepts and principles of the respiratory system is needed for the MCAT which we’ll outline below!
1. General Function and Respiratory Structure
The main function of the respiratory system is gas exchange, specifically the delivery of oxygen to blood and the elimination of carbon dioxide. Think of it like a combined mail/garbage disposal service: the “mail carrier” delivers oxygen while the “garbage disposal” removes carbon dioxide waste.
The respiratory system is somewhat organized in a hierarchical structure, similar to the muscle, which really begins at the trachea. The flow of O2 rich air follows the diagram below: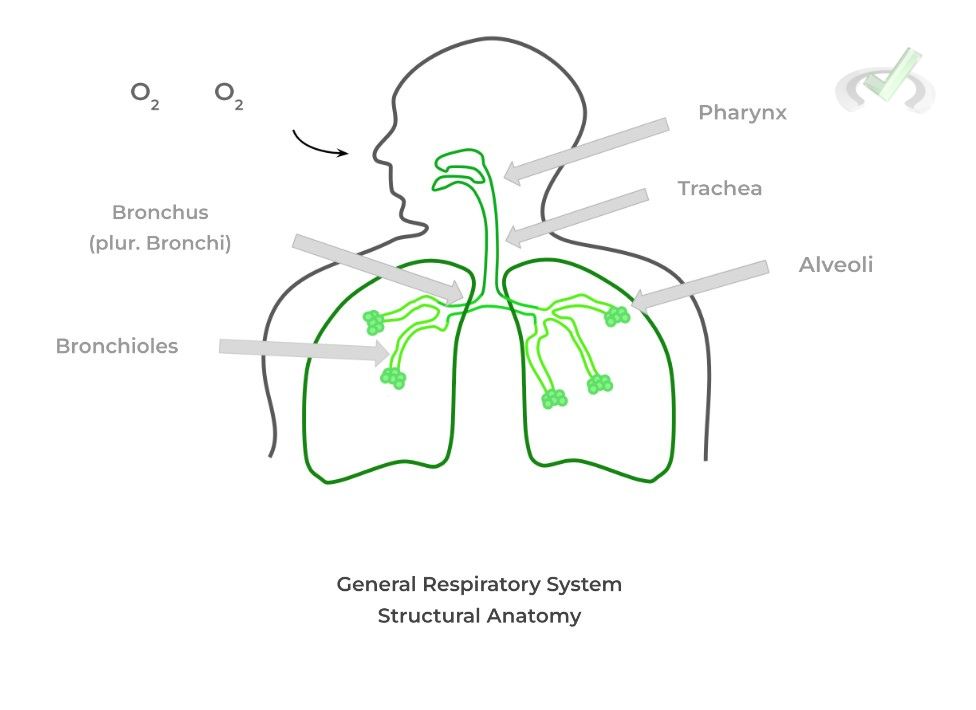
The alveoli is the primary site for gas exchange with the surrounding capillaries, where oxygen enters the bloodstream and carbon dioxide exits the bloodstream.
(Coming Soon!) Full Study Notes : Respiratory System: General Function and Respiratory Structure
For more in-depth content review on the respiratory system’s main function and anatomy, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
2. Breathing Mechanisms and Regulation
The process of breathing is actually governed by the flow of air down its pressure gradient, in a process called negative pressure breathing. Additionally, this is a perfect example of Boyle’s law which is a gas law stating there is an inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas.
As different muscles contract and relax in inhalation, the chest cavity and lungs expand and increase in volume, resulting in a decrease in the lungs’ air pressure due Boyle’s law.
Because the lung air pressure is lower relative to the outside air pressure, air moves into the lungs going down its pressure gradient. The reverse occurs for exhalation.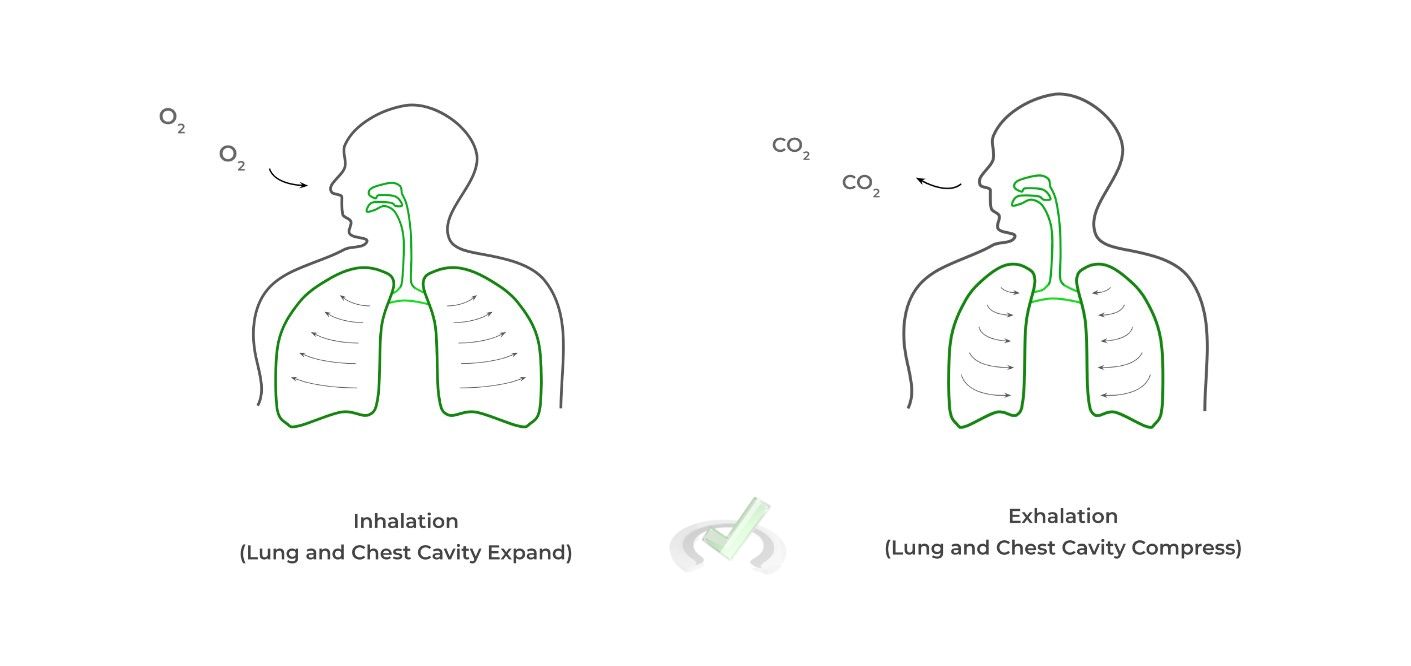
Breathing is also under nervous system control both voluntary and involuntary. In fact, blood pH is a primary stimulus for how the body regulates involuntary breathing.
This is because the amount of carbon dioxide with the blood can affect the pH of the blood which requires changes in breathing rate to return blood pH back to normal levels.
(Coming Soon!) Full Study Notes : Respiratory System: Breathing Mechanism and Regulation
For more in-depth content review on the mechanism and regulation of breathing, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
3. Functions Outside of Breathing
In addition to respiration, the respiratory system also has other functions including immune defense and thermoregulation thanks to other cells present within the respiratory tract.
The respiratory system is a great example of innate immunity as mucus lines the various respiratory vessels in order to trap any invading pathogens that have entered into the airway.
The epithelial cells lining the tracts have cilia extensions on their apical side which propels the mucus trapped pathogens towards the oral and nasal cavity to be coughed out, a process called the mucociliary elevator.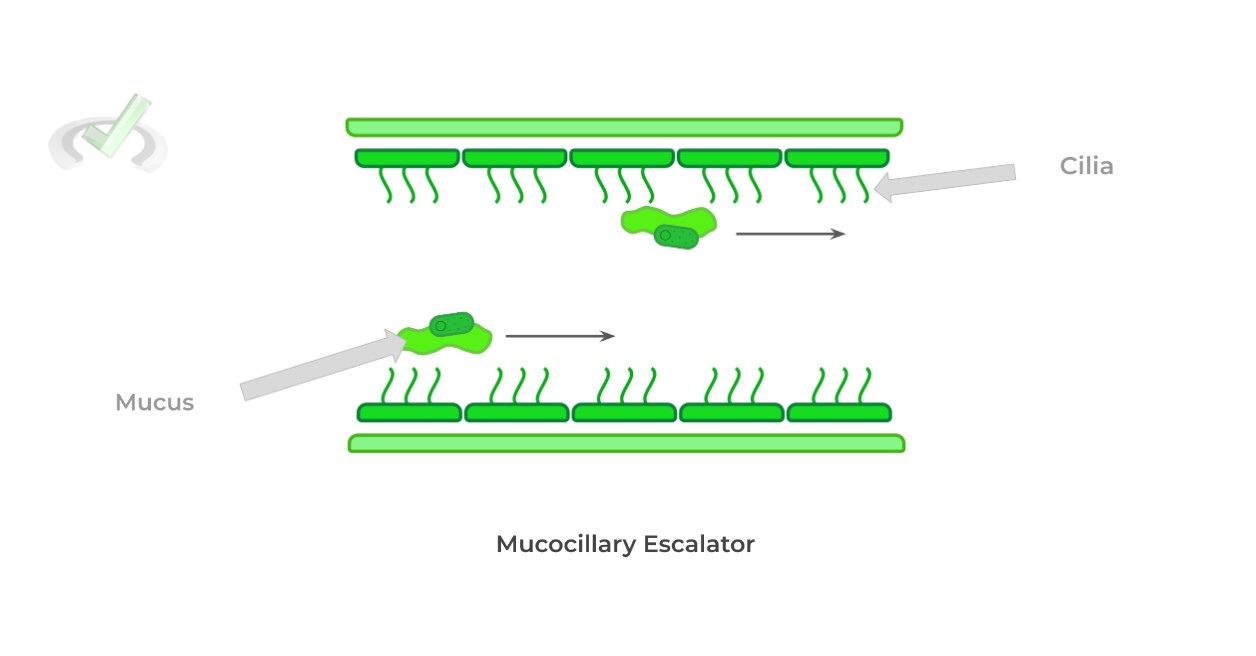
Additionally, exhalation can also help regulate our body temperature by dissipating excess heat, which is exactly the mechanism behind panting! After increased body temperature due to physical activity, the breathed in cooler air equilibrates as it warms up from the heat gained from the body.
This in turn causes the body to cool down as its heat is lost to the breathed in air. The warmed up air is then breathed out, dissipating the heat.
(Coming Soon!) Full Study Notes : Respiratory System: Functions Outside of Breathing
For more in-depth content review on the functions of breathing, check out these detailed lesson notes created by top MCAT scorers.
Important Definitions and Key Terms
Below are some high yield definitions and key terms to refer to when reviewing the immune system!
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Alveoli | Smallest division of the respiratory tract where gas exchange with the surrounding capillaries occur. |
Negative Pressure Breathing | Describes the mechanism of breathing where O2 rich air flows down its pressure gradient into the lungs. |
Boyle’s Law | Gas law which states there is an inverse relationship between the pressure of a gas and the volume it occupies. |
Mucociliary Elevator | Process where mucus trapped pathogens are directed upwards the respiratory tract via ciliary extensions from the respiratory epithelial cells to be coughed out. |
Additional FAQs - Respiratory System on the MCAT
A. What are the 7 Main Divisions of the Respiratory System – MCAT?
B. What is Tidal Volume – MCAT?
Additional Reading Links (Coming Soon!) – Study Notes for Respiratory Systems on the MCAT
Additional Reading: MCAT Biology Topics:
- Cells on the MCAT
- Digestive Systems on the MCAT
- Embryogenesis and Development on the MCAT
- Endocrine Systems on the MCAT
- Excretory Systems on the MCAT
- Genetics and Evolutions on the MCAT
- Immune Systems on the MCAT
- Nervous Systems on the MCAT
- Musculoskeletal Systems on the MCAT
- Reproduction on the MCAT
- Cardiovascular Systems on the MCAT


 To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these
To help you achieve your goal MCAT score, we take turns hosting these