If you have been researching and preparing for the MCAT, you might have noticed that most test-takers agree that one of the most effective ways to perform well on the MCAT is to answer practice questions.
Why? Answering MCAT practice questions acquaint you with how the questions are structured in the MCAT. At the same time, they help you gauge your MCAT readiness and help you identify the topics that you need to improve on.
In this article, we are providing you with some MCAT physics practice questions. Read on for more information.
What is MCAT Physics?
Physics is the study of the structure of matter and the interactions between its parts. It entails studying nature in all its macroscopic and microscopic manifestations. Most students believe that physics has the fewest medical applications out of all the sciences.
But physics has an impact on all aspects of life, including medicine. In rehabilitation hospitals, doctors frequently discuss the motion, forces, and bone strength with their patients.
In case you were wondering why physics is on the MCAT, now you know.
Physics questions can be found in the MCAT chem/physics section. There are 59 questions in this section, and physics is covered in 25% of them.
Physics knowledge and skills will be tested on 15 MCAT questions.
Summary Table of Physics Distribution in the MCAT
MCAT Section | Physics Subject | Percentage | Number of Questions (out of 59) |
|---|---|---|---|
Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems | Introductory Physics | 25% | 15 |
Total Number of MCAT Physics Questions: 15 | |||
Are MCAT Physics Questions Hard?
When it comes to how the question is presented on the MCAT for physics, it is pretty challenging and may leave you perplexed.
In terms of what you may assume, physics in college is more straightforward but more in-depth and mathematically demanding.
However, there is no need to worry that much. Answering the MCAT physics questions won’t be that tough if you are used to answering similar questions. That is where the importance of answering practice tests comes in.
Answer as many MCAT physics practice questions as possible before taking the MCAT. You will be surprised how much easier it is to understand the questions as you get used to taking them.
What Kind of Physics Questions are on the MCAT?
The types of questions in the MCAT physics vary depending on what the AAMC is trying to assess. Some questions will require a simple recall of terms and definitions, while others will test your higher-order and conceptual thinking skills.
Do not worry about the computations and MCAT physics equations too much. You will be fine if you know the formula for the required equation and know how to do simple math.
Do not forget the importance of the conversion of units as well, as some of the questions in the MCAT physics require your skills and knowledge about them.
Physics Topics to Study for the MCAT
As challenging as MCAT physics may seem, acing it and getting a commendable score is not impossible.
Just be mindful of the subjects you should research. Keep in mind that physics is a broad subject with a lot of disciplines to cover.
As you prepare for the MCAT, just focus on the following physics topics we have listed below:
MCAT Physics Practice Questions
No one would contest the fact that completing practice questions before the actual MCAT greatly helps test-takers.
By taking practice tests, you can become accustomed to the structure of the questions and the available options. At the same time, they evaluate your level of readiness and offer assistance in areas where you need it.
Get your paper and pencil ready. Here are a few MCAT physics practice questions for you to answer.
1. A man moves 30 meters east, then 40 meters north. What is the distinction between his displacement and his trip distance?
A. 0 m
B. 20 m
C. 50 m
D. 70 m
2. A 30 kg girl is seated on a seesaw two meters away from the pivot point. If her father weighs 90 kg, where must he sit to balance the seesaw?
A. 67 cm from the girl
B. 133 cm from the girl
C. 67 cm from the fulcrum
D. 267 cm from the fulcrum
3. Which of the following cannot be measured simultaneously, according to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle?
A. Direction and velocity
B. Placement and displacement
C. The first is speed and acceleration
D. The composition and rate of acceleration
4. Researchers perform a reaction and count the number of two products that result. In contrast to product 2, which both forms and destroys slowly, product 1 forms and degrades swiftly. Which of the following statements, correspondingly, best describes products 1 and 2?
A. kinetic, kinetic
B. kinetic, thermodynamic
C. thermodynamic, kinetic
D. thermodynamic, thermodynamic
5. The group 3 mouse receives 50 mg of oxaliplatin. How much of the medicine will still be in t the mouse after 24 hours if its half-life is 6 hours?
A. 1.562 mg
B. 3.125 mg
C. 6.250 mg
D. 12.50 mg
6. On top of a 15-meter long, 30° inclined lane, a 20 kg wagon is let go of its resting position. How is the frictional force impacted by increasing the angle of the slope, assuming there is friction between the wagon and the ramp?
A. The force of friction grows
B. Frictional force is reduced.
C. The amount of friction is unchanged.
D. The information provided does not allow for a determination.
7. A 10 kg wagon is at rest on an inclined plane with no friction. The plane's angle with the horizontal is 30°. How much effort is needed to prevent the wagon from falling off the plane on average?
A. 10 N
B. 49 N
C. 85 N
D. 98 N
8. An elevator is built to go upward at a speed of 5 m/s after an initial phase of acceleration and to support a weight limit of 9800 N (including its own weight). What connection exists between the maximum elevator cable tension and the maximum elevator weight as the elevator accelerates upward?
A. The tension is 9800 N.
B. There is less strain than 9800 N.
C. There is more tension than 9800 N.
D. The information provided does not allow for a determination.
9. A ball (m = 0.5 kg) is launched horizontally while a rock (m = 2 kg) is launched vertically. When both begin at the same height:
A. The ball will touch down first.
B. The rock will fall to the earth first.
C. The ball and rock will both fall to the ground simultaneously.
D. Before the ball and rock reach the earth, they will clash in the air.
10. A firefighter jumps horizontally, at a speed of 1.5 m/s, from a blazing structure. When is the angle between his acceleration and velocity vectors the largest?
A. Midway during his fall
B. Immediately after his launch
C. Upon reaching terminal velocity
D. Just before he touches down on the ground
11. Two positron decays, two gamma decays, and two alpha decays occur in a nuclide. What distinguishes the parent nuclide's atomic number from the daughter nuclide's atomic number?
A. 0
B. 2
C. 4
D. 6
12. While the half-life of carbon-12 is practically limitless, that of carbon-14 is around 5730 years. How ancient is a sample if the carbon-14 to carbon-12 ratio is 25% lower than the ratio that naturally occurs?
A. Around 5730 years
B. Around 11460 years
C. Less than 5730 years
D. Greater than 5730 years, but less than 11460 years
MCAT Physics Sample Passage 2
There are three main approaches to describing acids and bases. The most stringent definition is that provided by Arrhenius. It restricts acids and bases to types of molecules that release protons into a solution, and hydroxide ions, respectively. These bases include KOH and NaOH, whereas examples of acids include HCl and HBr. These acids undergo a dissociation reaction to reach equilibrium while in an aqueous solution.
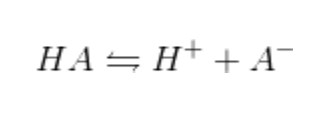
The bases all move forward in a similar way.
A more complete definition of an acid is provided by Brønsted-Lowry. Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases are not always Arrhenius acids and bases and vice versa. Arrhenius acids and Brønsted-Lowry acids both achieve equilibrium by the identical dissociation reaction, but the acid character is determined by distinct factors. Similar to the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition also includes conjugate bases, such as the A- in the preceding process, as hydroxide donors. A- receives the proton in the opposite process to regenerate HA. Thus, bases are defined as proton acceptors using the Brønsted-Lowry definition, whereas acids are defined as proton donors.
16. A scientist investigating the acid HA discovers that when the acid dissociates in solution, heat is produced. Which of the following is most likely true if the scientist increases the vessel's temperature after the reaction has reached equilibrium?
A. The level of A will rise in concentration.
B. The amount of HA will drop in concentration.
C. The amount of HA will rise in concentration.
D. There will be no change in the HA concentration.
17. A titration is used by a scientist to carefully add a base to the solution in order to study the acid HA. An acid-base titration reaches its equivalence point when…
A. The titrant has neutralized half of the acid.
B. The titrant has neutralized all of the bases.
C. The titrant has neutralized half of the base.
D. The titrant has completely neutralized the acid.
18. Chemical species can receive hydrogen ions from reducing agents like LiAlH4. In a solution, LiAlH4 will dissolve into hydrogen ions, which will then decrease the target substance. LiAlH4 must have which of the following characteristics in order to function as a reducing agent?
A. Since it gives protons rather than hydride ions, it is not an acid.
B. Since it contributes hydride ions rather than protons, it is not an acid.
C. Given that it gives protons rather than hydride ions, it must be an acid.
D. Since it contributes hydride ions rather than protons, it must be an acid.
MCAT Physics Sample Passage 3
On a hill covered in snow, two kids are having fun with their sleds. Sam is 50 kg and his sled is 10 kg in weight. Sally's sled weighs 12 kg and she is 40 kg. They arrive and use boots to ascend the hill. Sally trips halfway up the 50-meter incline and tumbles back to the bottom. Sam keeps going up, and when he reaches the summit, Sally follows.
Following that, they decide to sled down the hill, but they can't agree on who should go first.
Scenario 1:
Sam claims he will attain a higher velocity so he descends the hill first. Sam claims that they might have collided if Sally had gone first.
Scenario 2:
Sally claims she will feel less friction and hence reach a higher velocity if she descends the hill first. Sally claims that they might have collided if Sam had gone first.
Scenario 3:
Sam and Sally are unable to compromise, so they link a rope to each other and descend together.
19. What momentum does Sam have when he descends the 50-meter slope on his sled in Scenario 1 if the hill is frictionless?
A. 60 kg*m/s
B. 1,340 kg*m/s
C. 1,581 kg*m/s
D. 1,898 kg*m/s
20. John, a third boy, shows up to play on a nearby hill. Sally joins him in playing, and they discover that after sliding down the first hill, Sally was moving at a speed of 12 meters per second. John's speed was only 8 m/s. John's sled weighs 80 lbs. Which statement is accurate?
A. John has lower kinetic energy and Sally has less momentum.
B. John has more kinetic energy, but Sally has more momentum.
C. John has less kinetic energy and more momentum than Sally.
D. John has more kinetic energy than Sally, who has less momentum.
Answer Key:
1. B 11. D
2. C 12. C
3. A 13. B
4. B 14. A
5. B 15. D
6. B 16. C
7. B 17. D
8. C 18. B
9. A 19. D
10. B 20. A

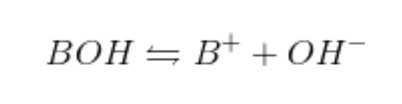

 To help you increase your MCAT score to the competitive mark quickly, we have collaboratively created these
To help you increase your MCAT score to the competitive mark quickly, we have collaboratively created these